Blog: Web Accessibility tips for Canvas - R.W.'s Blog 🏳️⚧️
Table of Contents
From: https://rachelwilshasingh.gitlab.io/teacher/
Related links:
- New rule on the Acccessibility of Web Content and Mobile Apps: https://www.ada.gov/resources/2024-03-08-web-rule/
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines: https://www.w3.org/WAI/WCAG22/quickref/?versions=2.1&showtechniques=253
1. R.W.'s quick tips sheet
- Prefer plaintext content for your courses as the primary resource.
- Plaintext can be read by screen-readers and read by students.
- Plaintext can be easily resized and reformatted to fit students' needs.
- Video, audio, and image content should be added afterwards as an alternative to that plaintext.
- Markdown (markdownguide.org) and HTML webpage formats can provide accessible plaintext with some visual of hierarchy, bulleted lists, etc.
- Canvas supports creating pages under the "Pages" section. You can edit it visually or with HTML markup.
- Utilize the different level of headers to distinguish sections and sub-sections of documents.
- When using color to differentiate things (e.g., parts of a graph), also use symbols to represent the differences.
- You can also look into Color Palettes for Colorblindness (davidmathlogic.com)
- Again, make sure to provide a description in plaintext for additional accessibility.
- Don't hide links behind text; provide the URL to items in the text if it's something that may be printed out.
- Student should be able to navigate webpage with keyboard only making use of the TAB key to switch between links/buttons and going between pages.
- Avoid flashing elements, such as a flashing background, avoid showing video clips that contain flashing lights.
2. WCAG guidelines that may be relevant to teachers
2.1. Text Alternatives (adding alt text):
Provide text alternatives for any non-text content so that it can be changed into other forms people need, such as large print, braille, speech, symbols or simpler language.
How to add good alt text:
- Describe the important parts of the image first. What are you trying to convey with the image?
- Any relevant information that needs to be taken from the image needs to be written in the alt text, or the information needs to be available in plaintext near the image. ("Screenshot of C++ code, which is given in the next example.")
- I describe if my images are screenshots, photos, drawings, etc. Per the Harvard page it says to also mention if it's a logo, illustration, painting, or cartoon, but don't need to say "image of", "picture of".
Resources:
In Canvas:
When uploading a new image in Canvas a space is provided for entering alt text.
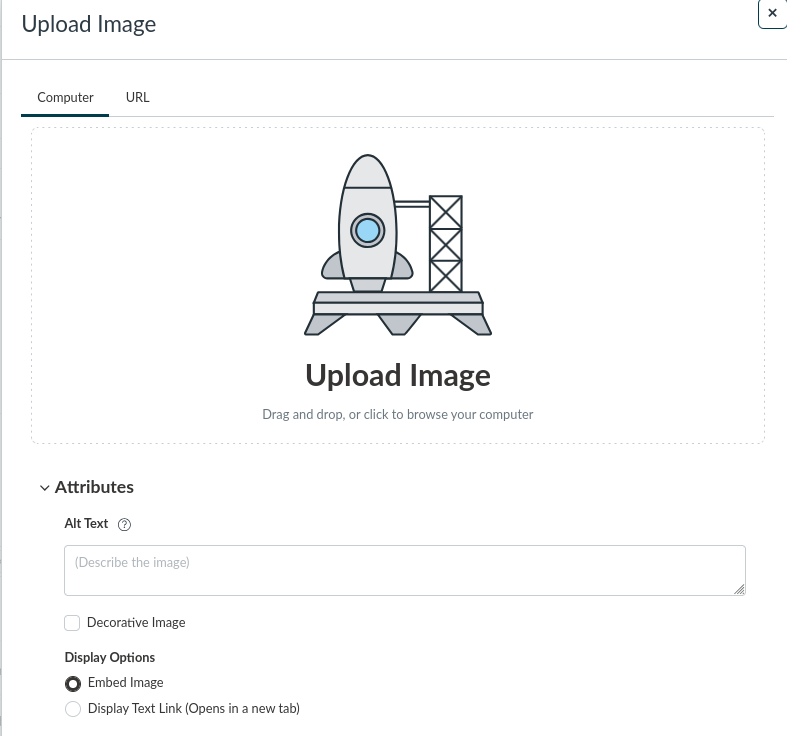
Figure 1: Screenshot of the Canvas "Upload Image" screen, including a space to add an image and a textbox to add Alt Text.
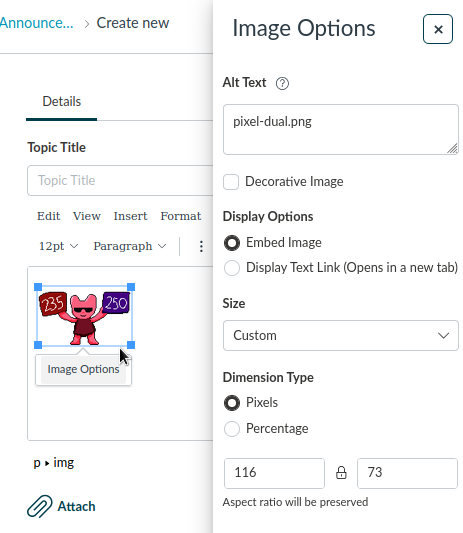
Figure 2: Screenshot of the Canvas "Image Options" pane, including the Alt Text field, Display Options, and Dimension Type.
2.2. Descriptions and captions for Audio and Video
Videos should have readable captions and audio should have transcripts so students can still access the content.
Visual items in the videos should also have text or audible descriptions available.
When in doubt, make plaintext content the primary resource and provide video and audio as alternatives.
WCAG:
- 1.2.2 - Captions (Prerecorded) - Captions are provided for all prerecorded audio content in synchronized media, except when the media is a media alternative for text and is clearly labeled as such.
- 1.2.3 - Audio Description or Media Alternative (Prerecorded) - An alternative for time-based media or audio description of the prerecorded video content is provided for synchronized media, except when the media is a media alternative for text and is clearly labeled as such.
2.3. Contrast and resizability
WCAG:
- 1.4.1 - Use of Color - Color is not used as the only visual means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element.
- 1.4.3 - Contrast (Minimum) - The visual presentation of text and images of text has a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 (See WCAG webpage for exceptions.)
- 1.4.4 - Resize Text - Except for captions and images of text, text can be resized without assistive technology up to 200 percent without loss of content or functionality.
- 1.4.5 - Images of Text
- 1.4.10 - Reflow - Content can be presented without loss of information or functionality, and without requiring scrolling in two dimensions for:
- Vertical scrolling content at a width equivalent to 320 CSS
- Horizontal scrolling content at a height equivalent to 256 CSS pixels;
2.4. Accessibility without a mouse
WCAG:
- 2.1.1 - Keyboard - All functionality of the content is operable through a keyboard interface without requiring specific timings for individual keystrokes, except where the underlying function requires input that depends on the path of the user's movement and not just the endpoints.
- 2.1.3 - Keyboard (No Exception) - All functionality of the content is operable through a keyboard interface without requiring specific timings for individual keystrokes.
2.5. Navigable
WCAG:
- 2.4.2 - Page Titled - Web pages have titles that describe topic or purpose.
- 2.4.4 - Link Purpose (In Context) - The purpose of each link can be determined from the link text alone or from the link text together with its programmatically determined link context, except where the purpose of the link would be ambiguous to users in general.
- 2.4.6 - Headings and Labels - Headings and labels describe topic or purpose.
- 2.4.10 - Section Headings - Section headings are used to organize the content.